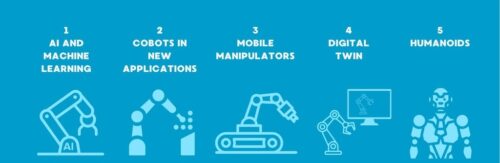
Robotics
Robotics refers to the study, design or equipment comprising robots. A robot is an automated enclosure of motion control devices traditionally designed for one purpose, though recent designs can more easily be reapplied in multiple applications. Collaborative robotics may work in proximity to humans. Mobile robots change locations to transport goods or affect changes to a process. Robot types often are defined by the type of arm(s) they have.
Robotics Articles
Robots are becoming more flexible and resilient
Advances in robotics and automation are making manufacturing and logistics companies of all sizes more productive, flexible and resilient.
Robotics insights
- Developments in hardware, software and artificial intelligence (AI) are making robots more flexible and resilient and able to perform more tasks in applications they couldnt’t before.
- Industries that stand to benefit the most include food and beverage, pharmaceutical, manufacturing, logistics and construction as companies are trying to fill labor shortages to keep operations running efficiently.
Offering the potential for faster, flexible, and more efficient production with less waste, robots can help companies be more adaptable and sustainable. Statistics from the 2021 World Robotics Report from the International Federation of Robotics (IFR) 2021 highlight a global increase in the rate of robot adoption, with robot density – calculated as the average number of robots per 10,000 workers – almost doubling between 2015 and 2020. Going forward, this growth is predicted to accelerate further, with estimates from research organization Research and Markets estimating annual market growth of 12.1% to 2030 to reach a value of more than $88 billion.
A driver for this growth will be the increased use of robots, as developments in technology – from software through to mobile robotics – open new possibilities for deployment in an expanded range of applications.
Ongoing developments in robotic hardware, software and AI technologies are opening new possibilities for deploying robots in manufacturing applications. Today’s robotic solutions can be used to achieve highly automated end-to-end manufacturing, with options encompassing everything from low payload cobots and fast picking Delta robots through to modular solutions and complete cells for handling multiple operations. The development of smart automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) is also helping to boost efficiency, enabling the seamless transfer of parts or sub-assemblies between different production stations, and ensuring that they are delivered where they need to be, on time and without error.
Globally, the benefits that this joined up approach to production can bring is seeing a steady growth across a variety of industries, including food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, electronics, logistics and construction as companies look for ways to integrate robots into their operations.
Innovations such as collaborative robots (cobots), simplified programming and user interfaces are also helping to make robots more accessible to SMEs. Cobots can help inexperienced users tackle the ‘low hanging fruit’ of simpler applications, with the experience gained enabling them to develop their understanding of what can be achieved with more complex set-ups.
Developments in programming and tools, such as block-based programming, now enable first time users to introduce robotic automation into their production lines without the need for specialist skills.
Software is also helping to address many of the pain points that have traditionally been associated with designing and commissioning robotic installations. Tools such as digital twins, virtual and Augmented Reality (AR) viewers, and offline programming and simulation mean companies can develop and test different configurations to find the best solution for their requirements. This ability to model and refine robotic processes to find the optimum configuration is particularly beneficial for industries subject to rapid changes in consumer demands, such as the food and beverage and logistics industries.
One of the benefits of robotic automation is its ability to enhance workforce productivity. Ongoing developments in robotic usability, performance and capabilities including vision, force control and path following have helped to broaden the applicability of robots across a range of tasks, enabling them to be used to fill gaps in workforces. In many cases, companies can also make better use of their existing skilled workforces by assigning lower value, dirty or more dangerous tasks to robots, releasing workers to handle other duties and/or higher levels tasks including supervising and programming the robot.
A robotic future
With many companies citing a shortage of expert robot operators as a key reason for not switching to robotic automation, there is a need to ensure that both current and future generations of workers can access the training they need to be able to use robots.
With this in mind, ABB has been developing its training programs to better prepare current and future generations for an age of increased automation. At a grassroots level, packages for schools, colleges and universities combine both robots and programming tools to equip students with the knowledge and experience needed to develop, build and maintain robotic solutions for manufacturing applications.
– This originally appeared on Control Engineering Europe’s website. Edited by Chris Vavra, web content manager, Control Engineering, CFE Media and Technology, cvavra@cfemedia.com.
Robotics FAQ
-
How is robotics used in manufacturing?
Robotics is used in manufacturing to automate repetitive, dangerous or precise tasks. Robotics can be used in different stages of the manufacturing process, such as material handling, assembly, welding, painting and inspection.
Robotic arms can be programmed to move in specific ways to handle and manipulate materials, such as picking and placing items on a conveyor belt or assembling parts. Robotics can also be used for welding and painting, which can be dangerous for humans to perform. They can also be used for precision tasks such as quality inspection and measurement.
In addition to performing specific tasks, robotics can also be used to increase productivity, improve product quality and reduce labor costs in manufacturing. Robotics can also increase manufacturing flexibility by enabling the production of a wide variety of products on a single production line.
-
What is the future of robotics in manufacturing?
The future of robotics in manufacturing is expected to involve greater automation, increased use of artificial intelligence and more advanced robotics technologies.
One major trend in the future of robotics in manufacturing is the increasing use of cobots, or collaborative robots, which are designed to work alongside humans in manufacturing environments. These robots are typically smaller and less expensive than traditional industrial robots and are designed to lower risk to nearby human workers, depending on the application.
Another trend is the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities into robotics systems. This will enable robots to learn and adapt to new tasks, improving their overall efficiency and performance.
Additionally, the development of advanced technologies such as 5G networks, IoT and cloud computing will enable robots to work together in a more coordinated and connected way, helping to increase the flexibility and scalability of manufacturing operations.
-
How has robotics improved manufacturing?
Robotics has improved manufacturing in several ways, including:
- Increased productivity: Robotics can work faster and more accurately than humans, which can increase the overall productivity of manufacturing operations.
- Improved product quality: Robots can be programmed to perform tasks with a high degree of precision and repeatability, which can help to improve the quality of manufactured products.
- Reduced labor costs: Robotics can automate repetitive and dangerous tasks, which can help to reduce labor costs and improve worker safety.
- Increased manufacturing flexibility: Robotics can be used to produce a wide variety of products on a production line, which can increase the flexibility of manufacturing operations.
- Improved safety: Robotics can perform dangerous tasks such as welding, painting and handling hazardous materials, reducing the risk of accidents and injuries to human workers.
- 24/7 operation: Robots can work long periods without downtime for maintenance, leading to a more efficient production processes.
-
What is robotics technology?
Robotics technology refers to the design, development, construction, operation and use of robots, as well as computer systems for their control, sensory feedback and information processing. It encompasses various fields including mechanical engineering, electrical engineering and computer science. Robotics technology is used in various applications, such as industrial manufacturing, military and defense, healthcare and entertainment.
Some FAQ content was compiled with the assistance of ChatGPT. Due to the limitations of AI tools, all content was edited and reviewed by our content team.