Digital Twin Consortium’s program uses maturity models and capability assessments to advance next-generation digital twins.
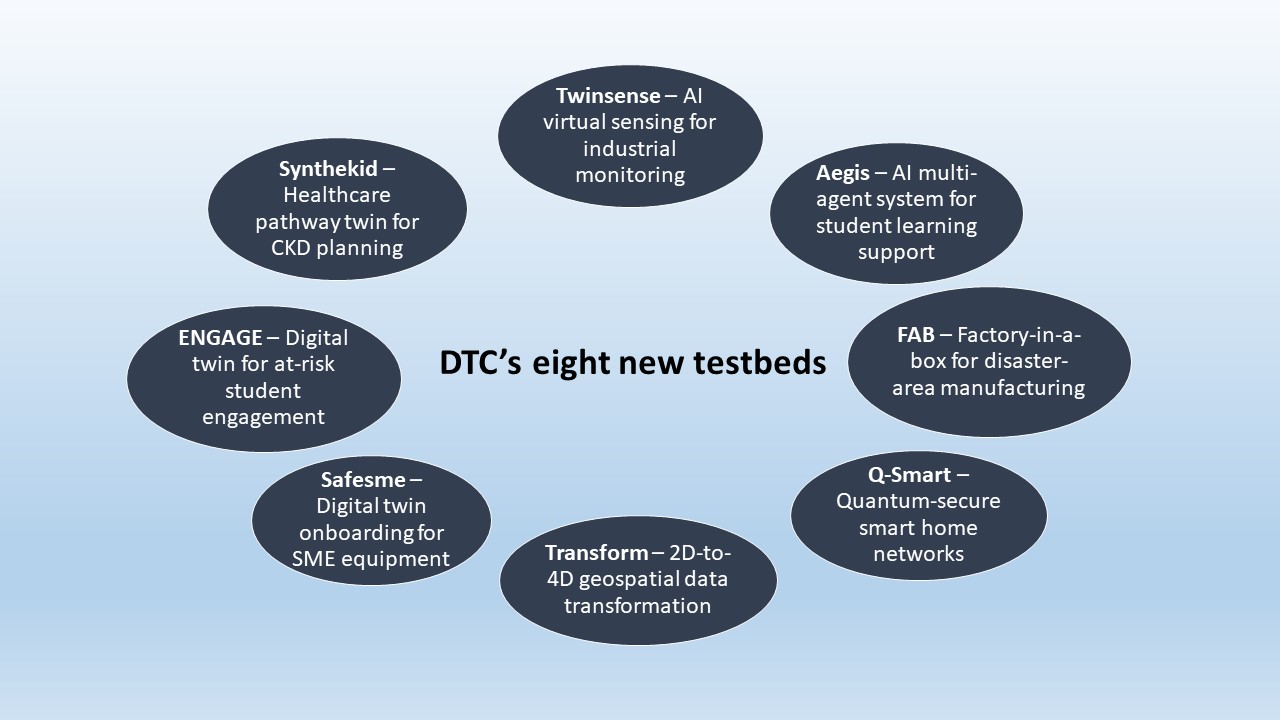
The Digital Twin Consortium (DTC) added eight testbeds to DTC Digital Twin Testbed Program, increasing the total to 16. Members can develop and test digital twin solutions, allowing participation in early-stage testbed development.
Dan Isaacs, GM and CTO of the DTC said: “We’re seeing strong interest from members worldwide in participating in our collaborative testbed program. Our members already utilize this program to develop and adopt AI-powered intelligent digital twins, generative AI digital twins, and other enabling technologies, advancing the core technologies that drive tomorrow’s digital transformation.”
DTC’s eight new member-led testbeds include:
- Twinsense: AI-based virtual sensing for real-time industrial monitoring
The Twinsense testbed demonstrates how digital twin technology can provide real-time virtual measurements of critical variables across industrial assets. It addresses challenge in monitoring hard-to-reach or costly-to- variables by leveraging digital twins for continuous virtual sensing. The testbed calibrates AI-based novelty detection systems using transfer learning, combing virtual and real-world data to enable proactive, AI-driven maintenance. Testing shows maintenance accuracy improved by 40%.
Lead developer: Aingura IIoT. Co-developer: XMPro - Aegis: AI system to support student learning
The testbed shows that multi-agent systems, trained on survey data from high-risk students, can identify factors that affect learning. It simulates intervention scenarios to help students respond to these factors, with the potential to improve engagement and reduce dropout rates. The testbed also assesses AI-powered interventions for personalized learning and dropout prevention.
Lead developer: My Performance Learning. Co-developer: Crysp - FAB: Factory-in-a-box for rapid disaster manufacturing
The testbed is a mobile, modular digital twin-enabled manufacturing unit that can produce critical energy components in areas affected by disaster. It helps lower transport costs, simplifies logistics and supports continued operation of systems and infrastructure. The unit enables local production with straightforward setup and allows remote coordination through a digital twin interface. Field-deployable, these production systems show that digital twin-enabled micro-manufacturing can operate in demanding environments.
Lead developers: DRG Solutions and Oak Ridge High School. Contributing technology providers: Oak Ridge National Laboratory. - Q-Smart: Quantum secure data exchange for resilient smart home cognitive networks
The Q-Smart testbed tests a home automation system built on decentralized, open-source components. It functions as a central control unit using wireless mesh networks, digital twins models, AI frameworks and XR interfaces for energy management and indoor air quality monitoring. The system performs processing locally and uses quantum-safe (PQC-ready) protocols for security. Self-learning algorithms adjust HVAC and ventilation settings to reduce energy use by up to 25%.
Lead developer: WINNIO. - Transform
The Transform testbed evaluates a framework that converts 2D data schemas into 4D geospatial representations with real-time updates. It supports standardized exchange across applications while preserving data accuracy during transformation. Tested with smart city infrastructure, the framework enables data transformation across transportation, utilities and emergency services systems.
Lead developer: EDX Technologies. Co-developer: Crysp. - Safesme: Smart asset fast enablement for SME equipment
The testbed applies digital twin commissioning and service functions on SME manufacturing equipment, including injection molding and packaging machines. It shows that SME-scale equipment can adopt digital twin onboarding and related service functions without high cost. The testbed supports automated onboarding and commissioning in under five minutes per asset, reduces setup time and operator workload, and preserves model consistency and API performance without requiring PLC upgrades or major development work.
Lead developer: HS Soft. - Early notification and guidance for academic growth and engagement (ENGAGE)
The testbed is focused on evaluating whether a digital twin can be applied to identify and support at-risk students. It will integrate academic scores, class participation, extracurricular involvement, behavioral indicators and sentiment analysis to capture engagement factors that are not usually measured in traditional monitoring systems but may relate to student retention.
Lead developer: Austin Community College District. - Synthetic healthcare pathway digital twin (Synthekid)
The testbed is designed to improve regional healthcare delivery using a digital twin that models chronic kidney disease (CKD) pathways across Yorkshire, UK. It examines how privacy-preserving digital twins can support healthcare planning, including scenario analysis and demand forecasting, while maintaining patient confidentiality. The platform also identifies intervention points by modeling patient pathways from early detection through disease progression, with the goal of informing care and system efficiency.
Lead developer: Health Innovation Network Yorkshire and Humber. Co-developers: Nexus, Counterpoint Technologies, Crysp.
The Digital Twin Testbed Program applies the DTC’s Composability Framework. It uses the Business Maturity Model, Platform Stack Architecture, and Capabilities Periodic Table, along with a maturity assessment framework that evaluates Generative AI, multi-agent systems and other advanced technologies.
Edited by Puja Mitra, WTWH Media, for Control Engineering, from a Digital Twin Consortium news release.