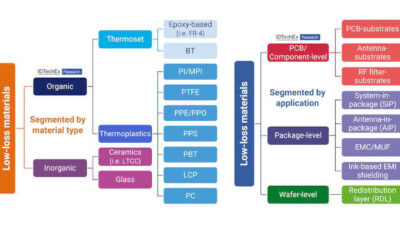
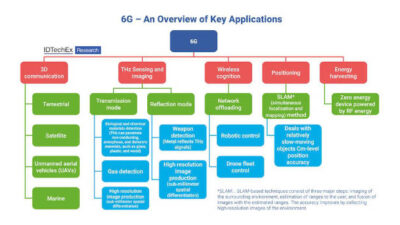
5G can help manufacturers realize a smarter factory with some adjustments and patience to realize its full potential. See three ways 5G can help manufacturing.
Learning Objectives
- Review benefits of 5G technologies for manufacturers.
- Examine three 5G examples for smart manufacturing: Monitoring, robotics, analytics.
- Consider how manufacturers can take full advantage of 5G in Smart Factories.
The rollout of 5G across the U.S. and around the world offers significant opportunities for manufacturers. The high speeds, improved connection stability and support for large numbers of devices in the same place make the technology perfect for businesses that have adopted Smart Factory systems.
Taking full advantage of 5G may require some realignment. This is what manufacturers should know about 5G and how it can integrate with their operations.
Benefits of 5G technology for manufacturers
5G is the next generation of cellular networking technology and the successor to 4G. Compared to its predecessor, 5G offers improved performance and more reliable connections in populated areas and big events, where many devices may be connecting to the same cell tower, according to T-Mobile’s 5G information.
It uses a few different technologies to achieve this, like massive MIMO (multiple input/multiple output), which helps cell towers handle connections from many devices simultaneously.
5G was developed and deployed in response to a growing need for fast internet connections and cell towers that could support many devices. The Internet of Things’ (IoT) rise caused a spike in the number of devices using cell networks to connect to the internet. 5G will help improve their performance.
Jen Jakobsen, development manager at HMS Labs, a business specializing in networked devices, believes 5G will be essential as manufacturing device fleets grow. While other networking solutions, like Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, have been effective for supporting this communication in the past, Jakobsen said, “The reliability of wireless Bluetooth is not sufficient. This is where 5G comes in.” The ultra-reliability and low-latency communications enabled by 5G make the technology a better fit for networking factory devices wirelessly.
Three 5G examples for smart manufacturing: Monitoring, robotics, analytics
Most manufacturers will take advantage of one or more of these key use cases for industrial 5G:
1. Remote monitoring and factory data collection: IoT sensors and monitors can allow businesses to capture a wide range of data on their facilities, workflows, factory systems and machinery. The right device in the right place can monitor everything from air quality to the lubrication of a robot arm, offering massive amounts of data when IoT fleets are large and specialized enough.
5G helps ensure data can flow from a fleet of IoT devices to the cloud, where monitoring systems can analyze it or deliver key numbers to managers via reporting tools or data dashboards.
These devices may require additional equipment to ensure connections remain stable. For example, EMI shielding is necessary for any device that transmits data wirelessly and will likely be essential for 5G-enabled factory technology, according to electromagnetic compatibility product provider Com-Power.
2. Collaborative robots (cobots): Many modern collaborative robots need an internet connection to function properly. Cloud computing resources enable faster processing, storage of valuable analytics data and easier integration with factory systems.
Wired connections guarantee some level of speed and reliability, but they can make robots less flexible and complicate the process of moving a cobot from one workstation to another. 5G offers these robots a connection to the cloud without wiring, allowing them to send important metrics there and use its resources for processing.
3. Predictive analytics for machines: Remote monitoring devices and networked machinery can be valuable sources of information for a business. In addition to real-time monitoring, according to ReHack Magazine, this data can be used with machine learning to enable advanced predictive analytics.
Predictive analytics tools use the data pools manufacturers gather to create powerful predictive models the business can use.
For example, historical sales data and warehouse inventory information can be used to create AI-powered demand forecasting models. They can help businesses accurately predict fluctuations in demand.
Another business may use information from machines to power a predictive maintenance model — software that can “predict when [an] asset will require maintenance and prevent equipment failure,” according to maintenance software company UpKeep. 5G helps keep these data sources connected so predictive models always have access to the most relevant details possible. For example, a predictive maintenance model can use real-time statistics from a machine to determine if failure is imminent or if repairs could help it perform more efficiently.
Ensuring devices are connected to the cloud and the predictive model has access to the information they gather will help a business get the most out of its data-collection device network.
How manufacturers can take full advantage of 5G in smart factories
The 5G rollout offers major opportunities for manufacturers. The high speeds, improved connection stability and support for large numbers of devices in the same place make the next generation of networking technology perfect for businesses that have adopted Smart Factory technologies.
While 5G may require some realignment in thinking, with some preparation it can be effectively integrated into industrial communications applications.
Devin Partida is a technology and manufacturing writer with work appearing at Manufacturing Tomorrow, Entrepreneur, Business2Community and www.DevinPartida.com. Edited by Mark T. Hoske, content manager, Control Engineering, CFE Media, [email protected].
KEYWORDS: 5G, industrial wireless, smart manufacturing
CONSIDER THIS
Are you examining 5G application advantages for smart manufacturing?