As industrial robots become more integral to manufacturing processes, ensuring their safe operation is crucial as well as making sure workers are protected.

Learning Objectives
- Identify safety risks related to industrial robots and how to implement strategies for risk mitigation.
- Learn about the latest safety technologies that help prevent accidents and improve robot-human interaction.
- Understand regulations governing industrial robot safety and learn how compliance ensures safety.
Robotic safety insights
- Industrial robot installations hit a record high in 2022, projecting further growth in 2024, highlighting automation’s pivotal role in manufacturing.
- Unexpected movements, system failures, collisions and electrical hazards pose significant risks in industrial settings, demanding robust safety protocols.
- Sensors, collaborative robots and software solutions enhance safety, enabling efficient human-robot collaboration while adhering to regulatory compliance and safety standards.
Industrial robots are becoming staples in manufacturing, changing the game by making production faster and more precise. In 2022, a record of 553,052 industrial robot installations was reported worldwide, marking a 5% growth rate year-on-year. The demand for industrial robots is projected to continue growing, with the International Federation of Robotics expecting 600,000 units to be installed worldwide this year.
With this rise, comes the importance of ensuring robots operate safely. To do this, users need to know about potential safety risks, how to implement risk mitigation strategies, the latest technologies for preventing accidents and the regulations that help keep everyone safe. Think of it as creating a safe space where humans and robots can work side by side, ensuring the push for automation doesn’t leave safety behind.

Understanding four common safety risks for industrial robots
Although industrial robots bring immense benefits, without proper safety measures, they can pose significant hazards. Four of the common safety risks associated with industrial robots are highlighted below.
1. Unexpected robot movements
Industrial robots, especially those with complex programming, can make unexpected movements. These unpredictable actions may happen due to programming errors or malfunctions, posing risks to nearby workers. For example, a painting robot in an automotive assembly line could unexpectedly extend its arm beyond the expected range due to a programming error. This could happen during a routine operation, putting nearby workers at risk if they inadvertently enter the robot’s operational zone without proper safeguards.
2. System failures
Like any complex machinery, industrial robots are not immune to system failures. These failures can lead to loss of control over the robot, potentially resulting in abrupt stops or erratic movements. For instance, a palletizing robot used in a warehouse to stack goods could experience a system failure due to worn-out components, leading to sudden and unpredictable movements.
3. Collision hazards
The interaction space between humans and robots in a shared workspace increases the risk of collisions. Collision hazards are particularly pronounced during manual programming, maintenance, or unexpected entries into the robot’s workspace.
In a mixed manufacturing environment, a mobile robot transporting materials could collide with a human worker if the worker unexpectedly steps into its path. Even with manual programming or maintenance checks, the risk is heightened without a clear distinction of the robot’s way, as well as the implementation of advanced detection systems to stop the robot’s movement when a human is detected too close.
4. Electrical hazards
Industrial robots are powered by high-voltage electrical systems, which pose risks of electric shock or fire. For example, an industrial welding robot, which requires high-voltage power to operate, might pose electrical hazards during maintenance or if there is an electrical fault. An electrician working on the robot without applying lockout/tagout procedures and devices could be exposed to electric shock.
Table 1: Industrial robot safety risks

Identifying these safety risks is the first step to mitigating and preventing them from happening.
Strategies for risk mitigation
Mitigating the risks we have identified involves a comprehensive strategy that includes risk assessment, implementation of preventive measures and adherence to safety protocols. These four risk assessment procedure are crucial:
-
Identify potential hazards: Conduct a thorough inspection of the robot’s work area to pinpoint possible sources of harm.
-
Evaluate the risks: Assess the likelihood and severity of identified hazards impacting workers or the production process.
-
Determine control measures: Develop strategies to eliminate or reduce the risks associated with each identified hazard.
-
Implement and monitor: Apply the control measures and monitor their effectiveness and adjusting as needed.
Preventive measure for ensuring robot safety
Integrating preventive measures into the robotic workspace is essential for minimizing safety risks. Safety guards and emergency stop buttons serve as immediate measures to stop robot operation in case of a hazard. Physical barriers, such as fences and light curtains, effectively delineate the robot’s operational zone, preventing unauthorized access and reducing the risk of accidental collisions. Implementing safety sensors and machine vision systems also can help in detecting the presence of humans within close proximity to the robot, triggering automatic shutdowns if necessary.
Safety protocols
Just as important are establishing comprehensive safety protocols. Training employees on safety practices and emergency response is crucial. This training should cover the proper operation of robots, awareness of the hazards they present, and the actions to take in an emergency. Regular drills and refresher courses ensure that safety remains at the forefront of workers’ minds and they are prepared to act in case of an incident. Creating a culture of safety where employees feel empowered to report potential risks and are encouraged to suggest improvements also can enhance safety.

Three advances in safety technologies
Advanced safety technologies have enhanced the capability to maintain secure environments in industrial settings where humans and robots collaborate. Below are some of these technologies:
1. Sensors and vision systems
Sensors and vision systems enable robots to accurately detect the presence of humans in their vicinity. This capability allows for real-time adjustments to a robot’s operation, such as slowing down or pausing movements, to avoid collisions or accidents. These systems are crucial in environments where robots and humans share workspaces, ensuring operations can proceed safely without compromising efficiency.
2. Collaborative robots (Cobots)
Collaborative robots, or cobots, are designed with human interaction in mind. These robots come equipped with features such as force limiters, which reduce the power and force behind their movements, making them safe to operate alongside humans. Cobots often re smaller and more agile with built-in safety mechanisms that allow them to sense contact and stop immediately to prevent injury. Their design prioritizes ease of use and safety, enabling them to be deployed in a variety of settings without the need for extensive safety barriers.
3. Software solutions
Advanced software enables continuous monitoring of robots, identifying anomalies that could indicate potential failures or hazards. Predictive maintenance software can forecast when parts are likely to fail and schedule repairs or replacements before any issues arise, reducing the risk of accidents. Furthermore, software can enforce safety protocols by ensuring robots operate within predefined safety parameters, automatically shutting down operations if risks are detected.
These advances in safety technologies are transforming the landscape of industrial robotics, making it possible to utilize the benefits of automation while ensuring the safety and well-being of human workers.
Three regulatory compliance and safety standards
Aside from the advanced technologies, regulations, and standards are ensuring the safety of using industrial robots in various workplaces.
1. OSHA and general industry standards
While the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has not established specific standards for robotics, it enforces general industry standards that apply to robotic operations. These include the control of hazardous energy, machinery and machine guarding, and electrical safety practices. Each state may also have different or more stringent requirements, reflecting the need for comprehensive safety protocols in environments with robots.
2. ANSI/RIA standards
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and the Robotic Industries Association (RIA) have developed safety standards specifically for industrial robots and robot systems. ANSI/RIA R15.06-2012, for example, addresses the safe design, installation, and integration of robot systems, including the requirement for a risk assessment methodology and the design of safeguarding systems. These standards, while voluntary unless adopted by regulation, are crucial for manufacturers, integrators, and users to ensure a safe workplace.
3. ISO standards
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) offers a suite of standards that cover various aspects of robot safety. ISO 10218-1 and ISO 10218-2 focus on the robot itself and the integration of robot systems. These standards provide guidelines for the design, operational modes, and safety features necessary to mitigate risks associated with industrial robots. Additionally, ISO/TS 15066 supplements ISO 10218 by providing detailed guidance on collaborative robot operation, emphasizing the importance of human-robot collaboration safety.
Table 2: Industrial robot safety standards and key aspects
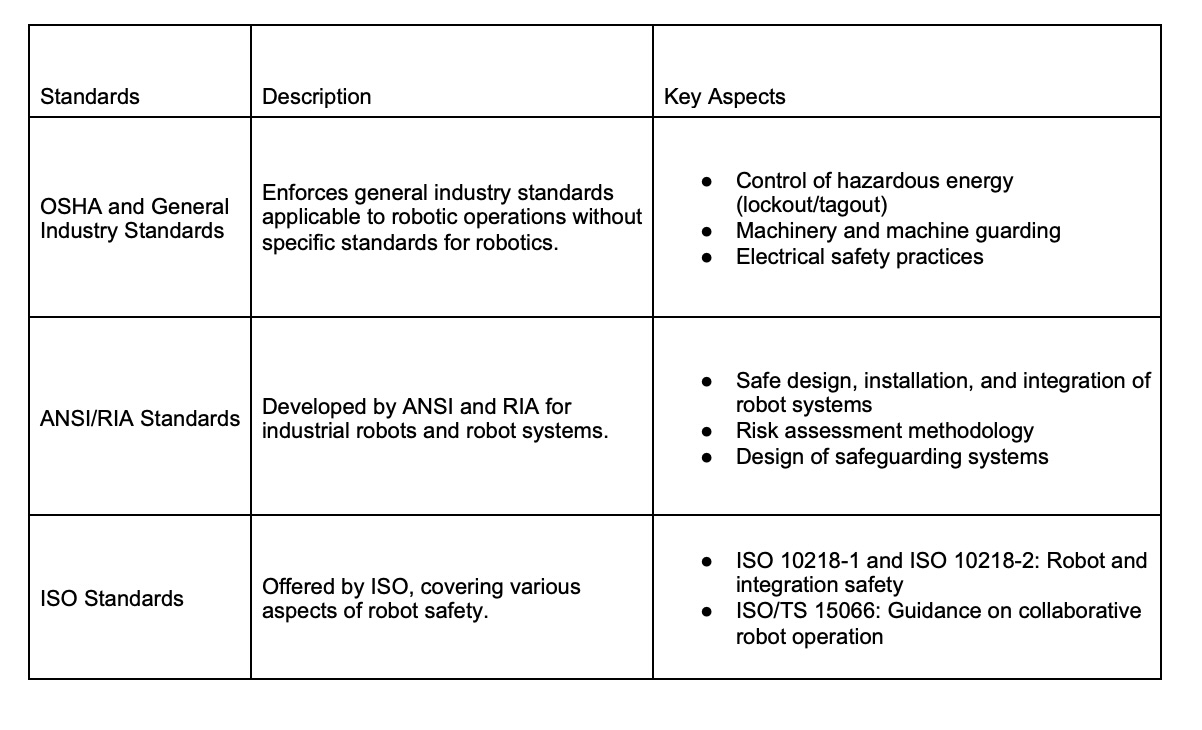
Adhering to these standards is a critical component of creating a safe working environment where humans and robots can effectively coexist. This helps companies not only protect their workers, but also enhance productivity and efficiency in their operations.
Ensuring worker, robot safety moving forward
In this era of fast-paced automation, ensuring safety is crucial. We should step up and integrate robust safety measures as we embrace automation technologies. It’s about striking the right balance: Pushing forward with technological innovations while making sure that safety will never be left behind. Let’s make sure that as we advance technologically, we never lose sight of the human element. Safety and innovation can, and should, go together.
Herbert Post is VP of health and safety at TradeSafe, a CFE Media and Technology content partner. Edited by Chris Vavra, senior editor, Control Engineering, WTWH Media, [email protected].
MORE ANSWERS
Keywords: robotics, machine safety
CONSIDER THIS
What are the biggest safety concerns you have with industrial robots?



