Interact Analysis reports shifting machinery trends as tariffs, tech demand, and regional investments reshape global sector performance.
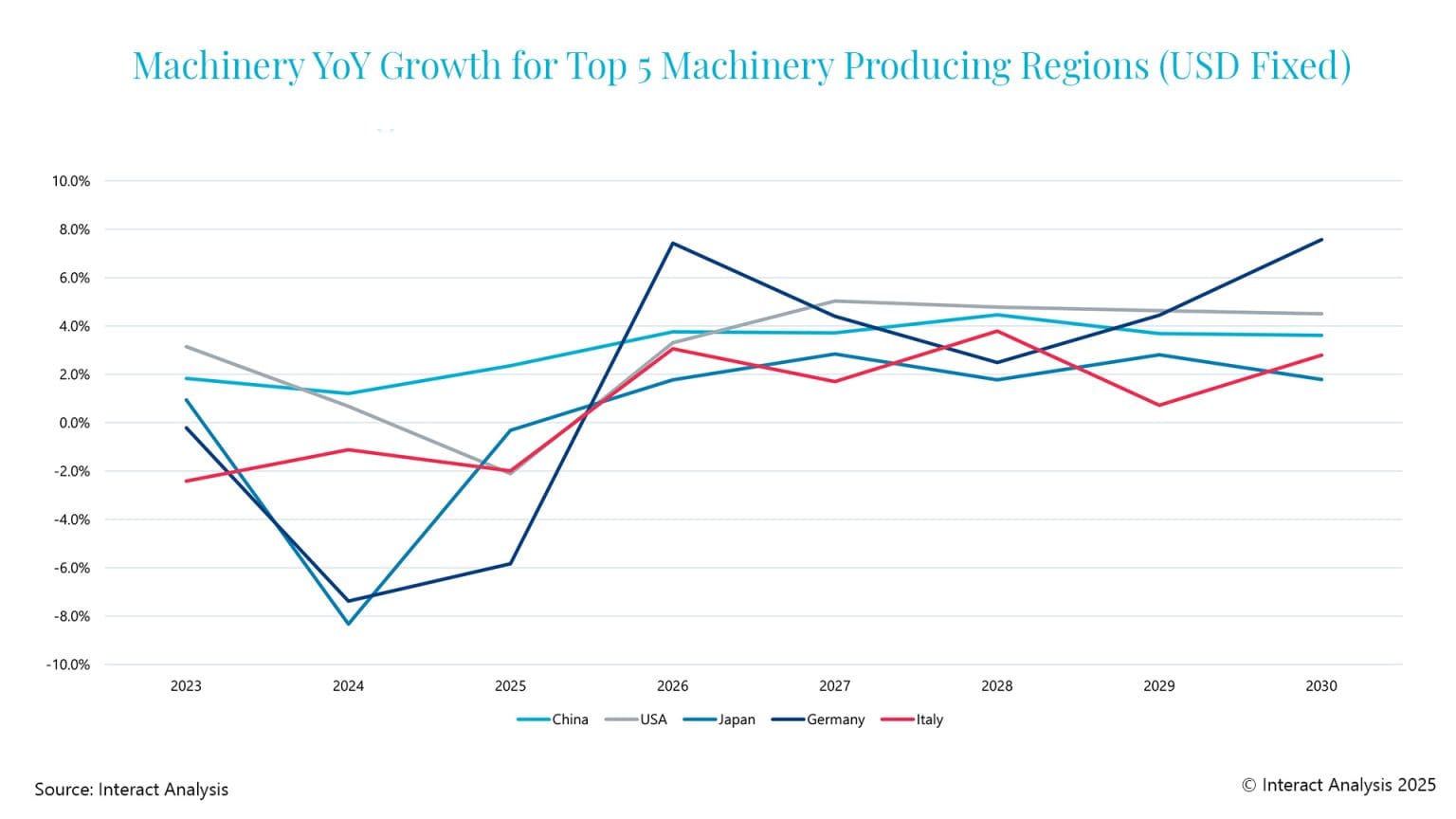
When analysing machinery market performance, two primary factors have influenced recent short-term forecasts from the Interact Analysis Manufacturing Industry Output (MIO) Tracker. Machinery production has been affected by elevated interest rates and increased inventory levels. In 2024 and 2025, destocking efforts have contributed to a slowdown in production. However, trends varyacross sectors. Areas such as packaging machinery, mining and quarrying, and semiconductor and electronics machinery production are projected to perform relatively well, supported by ongoing technological developments, energy transition and macroeconomic factors.
How are US tariffs impacting machinery markets in Asia?
Although Japan experienced moderate growth early in the year, tariffs are projected to exert downward pressure on the Asian market. In South Korea, machinery investment —including in the semiconductor —declined in early 2025. However, this may be a short-term trend, as capital goods import and machinery orders have started to increase. In China, most machinery is consumed within the domestic market, which may reduce the potential effects of external tariffs.
What is the current packaging machinery outlook for 2025?
Factory expansions in India, Vietnam and Mexico are projected to contribute to increased demand in the global packaging machinery sector, along with potential growth from near-shoring to the United States. Demand is influenced by factors such as technological advancements (including AI, IoT and predictive maintenance), sustainability requirements, and cost constraints. Manufacturers are seeking equipment that supports frequent changeovers and can handle diverse product types. In Europe, regulatory requirements like the EU Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR) are prompting investment in sustainable machinery. In the United States, Food and Drug Administration (FDA) guidelines are placing more emphasis on tamper-evident features for packaging in food and pharmaceutical applications.
What is the current semiconductor and electronics machinery outlook for 2025?
Three primary factors currently influencing the semiconductor industry include increased use of AI, adoption of 5G, and growing demand from electric vehicles. Some of the largest semiconductor equipment manufacturers – such as ASML, Applied Materials, and Tokyo Electron – are undergoing significant capacity expansions. There are currently 18 new semiconductor fabrication projects preparing for machinery procurement across the United States, China, Japan, Taiwan, and Europe. In some regions, governments are supporting accelerated semiconductor production growth because by providing incentives to relocate manufacturing operations domestically, viewing it as a matter of national security. Data from the MIO Tracker indicates that a significant share of semiconductor production is based in Asian countries, particularly China (23%), Japan (20%), and South Korea (13%).
What is the current mining and quarrying machinery outlook for 2025?
Increased use of electric vehicles, wind turbines, and battery storage has contributed to growth in critical minerals mining and supported expansion in the tunnelling and extraction equipment markets. There is growing demand for mining and quarrying machinery in regions such as Australia and Canada, which contain keyminerals for energy transition, including copper, cobalt, and lithium.
China is the leading producer of rare earth minerals and accounts formore than 40% of global mining machinery output. The US has granted FAST-41 status to 10 domestic mining projects in an effort to increase mineral production. These projects aim to reduce dependence on imported materials, support employment, and contribute to economic activity. However, tariffs on steel and aluminium may increase machinery production costs in the US.
What is the current machine tools outlook?
There are near-term challenges for the machine tools sector, though some projections suggest stabilization over the longer term. In North America, US tariffs and decreased demand have led some manufacturers to reduce output. The long-term effect of these trade measures will depend on whether there is a sustained increase in domesticmetals and automotive production.
China continues to lead in machine tool production by volume, while India is steadily increasing its capacity. The global market for machine tools is expected to declineslightly in 2025, reflecting ongoing structural challenges such as the transition away from internal combustion engine technologies. In Europe, rising defense spending could drive greater demand for regionally produced equipment, potentially supporting future demand for machine tools.
What is the current outlook for textile machinery?
China remains the largest producer of textile machinery, accounting for 60% of global output. Apparel production is shifting toward India, Vietnam and Bangladesh, which has contributed to rising demand for textile machinery in regions such as Turkey and India. In 2015, India accounted for 4% of global textile machinery production, with a MIO production value below $2 billion. By 2025, this share is projected to reach 8%, with a production value of approximately $4 billion. During this period, India is expected to move from fifth to second in global production rankings.
Final thoughts
Tariffs in the United States have resulted in a slowdown in new machine orders, with businesses expressing uncertainty due to shifting tariff policies. Similar to trends observed during the 201 tariffs in 2018, new orders may increase ahead of the July 10 enforcement date, followed by a potential decline that could impact overall production. Several European markets are showing weak performance, with data from January and February indicating notable year-on-year declines. For example, German agriculture, mining, and textile machinery sectors each contracted by at least 10%, with Italy and France experiencing comparable reductions.
However, growth patterns vary by regions and machinery sectors. China’s industrial sector is projected to begin recovering in 2025, with further improvement expected in 2026, which may support the country’s machinery sector. Semiconductors, mining and quarrying, and packaging are currently experiencing growth influenced by specific industry drivers. The final structure of US trade tariffs remains undetermined, making it difficultto fully assess their potential impact. Overall, the 2025 machinery manufacturing outlook remains uncertain.
Interact Analysis’ Manufacturing Industry Output (MIO) Tracker forecasts out to 2028 and covers a total of 45 countries, across 72 manufacturing end user sectors, 30 machinery sectors and two points in the supply chain (machinery and manufacturing end-users). To learn more, get in touch with Jack Loughney directly.
Edited by Puja Mitra, WTWH Media, for Control Engineering, from an Interact Analysis news release.



